Kin Against Kin: Internal Co-selection and the Coherence of Kinship Typologies.
Authors:
Citation:
Details:
Published: 6 June, 2021.
Download:
Abstract:
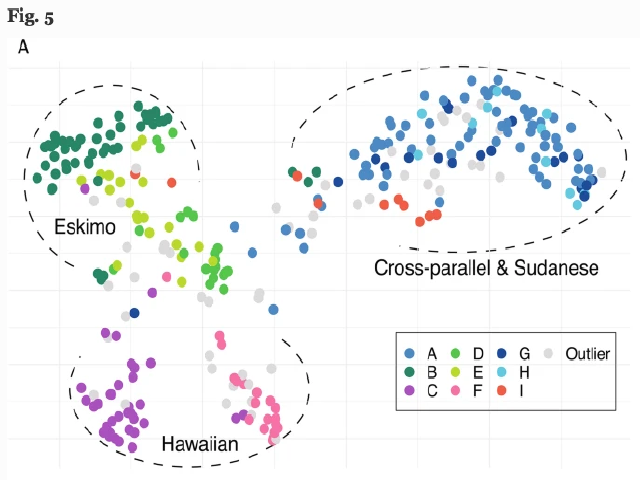
Across the world people in different societies structure their family relationships in many different ways. These relationships become encoded in their languages as kinship terminology, a word set that maps variably onto a vast genealogical grid of kinship categories, each of which could in principle vary independently. But the observed diversity of kinship terminology is considerably smaller than the enormous theoretical design space. For the past century anthropologists have captured this variation in typological schemes with only a small number of model system types. Whether those types exhibit the internal co-selection of parts implicit in their use is an outstanding question, as is the sufficiency of typologies in capturing variation as a whole. We interrogate the coherence of classic kinship typologies using modern statistical approaches and systematic data from a new database, Kinbank. We first survey the canonical types and their assumed patterns of internal and external co-selection, then present two data-driven approaches to assess internal coherence. Our first analysis reveals that across parents’ and ego’s (one’s own) generation, typology has limited predictive value: knowing the system in one generation does not reliably predict the other. Though we detect limited co-selection between generations, “disharmonic” systems are equally common. Second, we represent structural diversity with a novel multidimensional approach we term kinship space. This approach reveals, for ego’s generation, some broad patterning consistent with the canonical typology, but diversity (and mixed systems) is considerably higher than classical typologies suggest. Our results strongly challenge the descriptive adequacy of the set of canonical kinship types.